1. Quick Sort란?
- Quick Select와 마찬가지로 정렬이 되어있지 않은 배열을 대상으로 사용하는 알고리즘이다.
- Quick Select와 동일하게 Partitioning을 이용하여 배열을 정렬한다.
a) Quick Sort 정렬과정

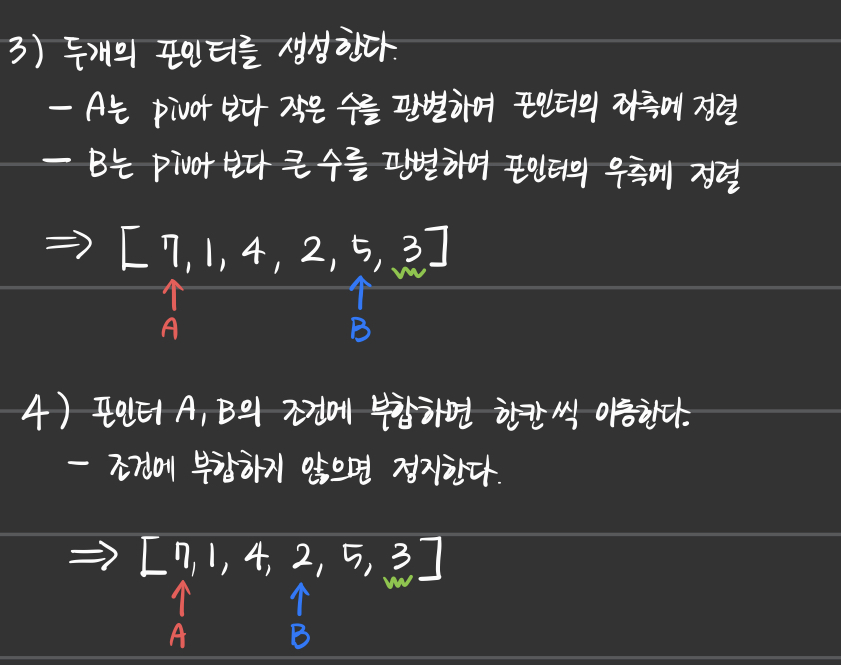



b) Quick Sort의 시간복잡도


c) Quick Sort의 안정성(Stability)
- Quick Sort는 불안정한(unstable) 정렬 알고리즘이다.
2. 코드구현
from typing import List
import random
def quick_sort(case:List[int], begin_idx:int, last_idx:int) -> List[int]:
length = last_idx - begin_idx + 1
if length <= 1:
return case
pivot_idx = random.randrange(begin_idx, last_idx + 1)
case[pivot_idx], case[last_idx] = case[last_idx], case[pivot_idx]
left_idx = 0
right_idx = last_idx - 1
pivot = case[last_idx]
while left_idx <= right_idx:
if case[left_idx] <= pivot:
left_idx += 1
continue
if case[right_idx] > pivot:
right_idx -= 1
continue
if pivot < case[left_idx] and pivot >= case[right_idx]:
case[left_idx], case[right_idx] = case[right_idx], case[left_idx]
continue
case[left_idx], case[last_idx] = case[last_idx], case[left_idx]
# pivot의 우측 파티션을 대상으로 quick sort 적용
quick_sort(case = case, begin_idx = left_idx + 1, last_idx = last_idx)
# pivot의 좌측 파티션을 대상으로 quick sort 적용
quick_sort(case = case, begin_idx = begin_idx, last_idx = left_idx - 1)
return case
case = [5, 7, 9, 3, 1, 5, 5, 2, 4]
quick_sort(case = case, begin_idx = 0, last_idx = len(case) - 1)
print(case)
3. Quick Sort 분석
a) Quick Sort와 Select의 차이
- Quick Select는 이름 그대로 특정한 수를 선택(Select)하기위한 알고리즘이다.
- 그러므로 어떤 조건에 맞는 특정한 요소 하나를 반환한다.
- Quick Sort는 Quick Select와 다르게 정렬을 위한 알고리즘이다.
- 그러므로 배열을 반환한다.
'Algorithm > 알고리즘 공부노트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 9. Array(배열) - Heap Sort(2) (0) | 2021.09.09 |
|---|---|
| 8. Array(배열) - Heap Sort(1) (0) | 2021.09.09 |
| 6. Array(배열) - Quick Select (1) | 2021.09.02 |
| 5. Array(배열) - Merge Sort(병합정렬) (0) | 2021.08.31 |
| 버블정렬, 삽입정렬, 선택정렬 완전분석 (0) | 2021.08.30 |




댓글